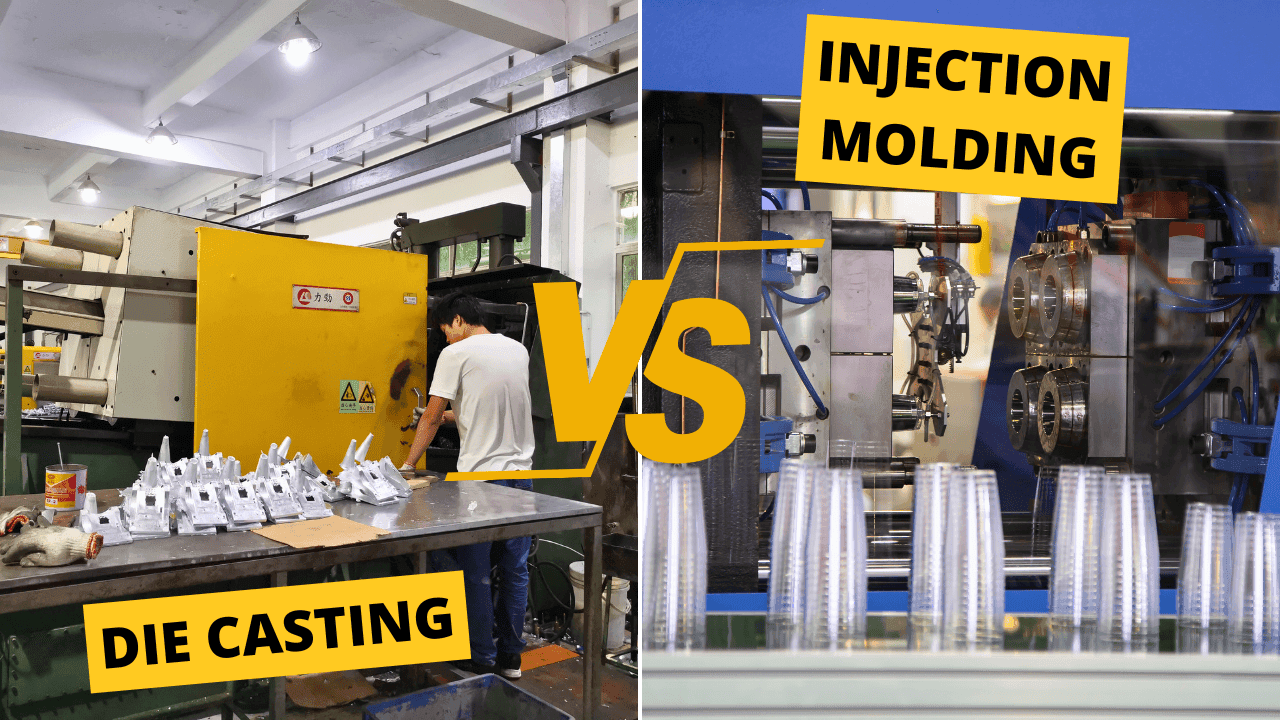
Have you ever wondered how metal and plastic objects are made? Two common ways to shape materials are Die Casting and Injection Molding. These methods help create everything from car parts to toy figurines. Let’s explore how they work and which one is better for different products.
1. What’s the Difference Between Die Casting and Injection Molding?
Both processes use molds to shape materials, but they are different in many ways.
| Feature | Die Casting (for metals) | Injection Molding (for plastics) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Used | Metal (Aluminum, Zinc, Magnesium) | Plastic (ABS, PC, Nylon, etc.) |
| Temperature | Over 600°C (very hot!) | Around 150-300°C |
| Mold Cost | High (must withstand heat & pressure) | Lower (easier to make) |
| Single Product Cost | Higher (metal is expensive) | Lower (plastic is cheaper) |
| Precision | Very accurate (±0.05mm) | Less accurate (±0.1mm or more) |
| Surface Finish | May need extra work (polishing, coating) | Smooth, usually ready to use |
| Common Uses | Car parts, electronics, smartwatches | Toys, phone cases, home appliances |
💡 Easy Example
- Die Casting is like a metal cake mold, where hot liquid metal is poured in and hardens.
- Injection Molding is like melting plastic into a shape, then letting it cool.
2. Cost: Which One is Cheaper?
✅ Mold Cost
- Die Casting molds are expensive because they must handle extreme heat and pressure.
- Injection Molding molds are cheaper because plastic is easier to shape.
✅ Cost Per Product
- Die Casting: More expensive per piece due to metal costs.
- Injection Molding: Less expensive because plastic is cheaper and reusable.
👉 Conclusion: If you need a lot of products, die casting is worth the high mold cost. If you want affordable mass production, injection molding is better.
3. Precision & Quality: Which One is More Accurate?
- Die Casting is more precise (±0.05mm), great for detailed metal parts.
- Injection Molding can shrink slightly (±0.1mm+), causing small shape changes.
- Die Casting parts may need extra work (polishing, coating).
- Injection Molded parts are smooth and ready to use.
4. Where Are These Methods Used?
| Industry | Die Casting | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Cars | Engine parts, metal housings | Plastic dashboards, interior parts |
| Electronics | Laptop frames, smartwatch cases | Phone cases, chargers |
| Wearables | VR headset frames, watch frames | Plastic bands, headphone cases |
| Home Appliances | Fan covers, metal heat sinks | TV cases, plastic shelves |
👉 Conclusion:
- Need strong and precise metal parts? Choose Die Casting.
- Need lightweight, low-cost plastic parts? Choose Injection Molding.
- Some products use both! (Example: smartwatches have a metal case and a plastic strap.)
5. Which is More Eco-Friendly?
- Die Casting: Metals can be recycled but need a lot of energy to melt.
- Injection Molding: Some plastics can be recycled, but not all (like PVC).
👉 Conclusion: Injection molding is greener, but only if plastics are recycled properly.
6. Which One Should You Choose?
| Feature | Best for Die Casting | Best for Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Strong & Durable | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Lightweight | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| High Precision | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Low Cost | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Mass Production | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
👉 Summary: Both methods are great, but the right choice depends on the product.
📌 Final Thoughts
Die Casting or Injection Molding? Metal or Plastic? Knowing the differences helps us make smarter choices in manufacturing!
💡 What do you think? Which process do you think is better? Have you seen products made with these methods? Share your thoughts!